How to use NexoBrid®
NexoBrid is a first-line enzymatic agent indicated for eschar removal in adults with deep partial thickness (DPT) and/or full thickness (FT) thermal burns.1,2
NexoBrid can be applied as a 4-hour application within hours of patient presentation for earlier and more informed medical planning for healing and care. NexoBrid must be removed after 4 hours.1,3,4
NexoBrid may be applied to an area of up to 15% body surface area (BSA) in one application.1
- If the wound area is more than 15% BSA, apply NexoBrid in 2 separate sessions (e.g., treat up to 15% BSA in one session and up to 5% BSA in a second session)1
- The total treatment area must not exceed 20% BSA across two treatment sessions1
- Apply the second application of NexoBrid twenty-four (24) hours after the first application to the same or new burn wound area1
- Use pain management as practiced for an extensive dressing change of burn wounds 15 minutes prior to all NexoBrid-related procedures
NexoBrid Preparation1
NexoBrid is only to be administered by a healthcare professional.
Precautions should be taken to avoid exposure during preparation and handling (e.g., gloves, surgical masks, other protective coverings, as needed). In the event of inadvertent skin exposure, rinse NexoBrid off with water to reduce the likelihood of skin sensitization.
- Gather the following supplies prior to NexoBrid preparation and application. All supplies should be sterile:
- Instrument for mixing (e.g., spatula or tongue depressor)
- Tongue depressor for NexoBrid application
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Irrigation
- Occlusive film dressing
- Loose, thick fluffy dressing and bandage
- Maintain pain management throughout the application as practiced for an extensive dressing change of burn wounds. At least 15 minutes prior to NexoBrid application, ensure adequate pain control measures are in place to address NexoBrid-related pain
Wound Preparation, Cleansing, and Soaking1
- Thoroughly clean the wound to remove any charred tissue, blisters, and any topical products
- Keratin isolates the eschar from direct contact with NexoBrid and prevents eschar removal5
- Eschar saturated with topical medicinal products and their remains (e.g., silver-based products or povidone iodine) can interfere with the activity of NexoBrid and decrease its efficacy5
- Apply a dressing soaked with an antibacterial solution to the treatment area for at least 2 hours
- Ensure the wound bed is clear of any remnants of topical agents (e.g., silver sulfadiazine or povidone iodine)

Product illustration
NexoBrid can be applied to up to 15% BSA in one application.1
- The total treatment area must not exceed 20% BSA across two treatment sessions1
- A second application of NexoBrid may be applied 24 hours after the first application to the same or new burn wound area1
Nexobrid Mixing1
- Prepare NexoBrid at the patient’s bedside within 15 minutes of the intended application
- Using aseptic technique, mix NexoBrid lyophilized powder and gel vehicle as follows:
- Pour the NexoBrid lyophilized powder into the gel vehicle jar
- Thoroughly mix the NexoBrid lyophilized powder and gel vehicle using a sterile instrument (e.g., tongue depressor or spatula) until the mixture is uniform
- The mixed lyophilized powder and gel vehicle produce NexoBrid in a final concentration of 8.8%
- Discard NexoBrid if not used within 15 minutes of preparation, as the enzymatic activity of the product decreases progressively following mixing
Wound Preparation1
- Apply an ointment skin protectant (e.g., petrolatum) 2 to 3 cm outside of the treatment area to create an ointment barrier
- Protect any open wounds (e.g., laceration, abraded skin, and escharotomy incision) with skin protectant ointments or ointment gauze to prevent possible exposure to NexoBrid
- Avoid applying the ointment to the treatment area itself, as this would impede direct contact of NexoBrid with the eschar
Application of NexoBrid1
- Apply NexoBrid within 15 minutes of preparation as follows:
- Moisten the treatment area by sprinkling sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Irrigation onto the burn wound
- Using a sterile tongue depressor, completely cover the moistened treatment area with the mixed NexoBrid in a 3 mm thick layer (approximate thickness of a tongue depressor) that completely covers the burn wound area
- Cover the treated wound with a sterile occlusive film dressing
- Gently press the occlusive film dressing at the area of contact with the ointment barrier
- Ensure adherence between the occlusive film dressing and the sterile ointment barrier
- Achieve complete containment of NexoBrid on the treatment area
- NexoBrid gel should fill the entire volume of the treatment area
- There should be no visible air under the occlusive film dressing
- Position patient to minimize movement and avoid pressure on the treatment area during treatment time6
- NexoBrid will liquify as enzymatic process begins
- Care should be taken to keep gel vehicle in place
- Monitor throughout application for continuous coverage
- Cover the dressed wound with a sterile loose, thick, fluffy dressing and secure with a sterile bandage
- Leave the dressing and NexoBrid in place for 4 hours
- Discard any unused portions of NexoBrid
Monitoring1
- Monitor patients for signs of local or systemic allergic reactions. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, remove NexoBrid (if applicable) from the treatment area and initiate appropriate therapy
Select IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with postmarketing use of anacaulase-bcdb.
Coagulopathy
Avoid use of NexoBrid in patients with uncontrolled disorders of coagulation. Use with caution in patients on anticoagulant therapy or other drugs affecting coagulation, and in patients with low platelet counts and increased risk of bleeding from other causes. Monitor patients for possible signs of coagulation abnormalities and signs of bleeding.
- Implement and maintain pain management as practiced for an extensive dressing change of burn wounds throughout the following removal procedure
- Remove NexoBrid after 4 hours
- Gather the following supplies prior to NexoBrid removal. All supplies should be sterile:
- Blunt-edged instruments (e.g., tongue depressor)
- Large dry gauze
- Gauze soaked with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Irrigation
- Dressing soaked with an antibacterial solution
- Remove the occlusive film dressing using aseptic technique
- Remove the ointment barrier using a sterile blunt-edged instrument
- Remove the dissolved eschar from the wound by scraping it away with a sterile blunt-edged instrument
- Wipe the wound thoroughly with a large sterile dry gauze
- Then wipe with a sterile gauze that has been soaked with sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Irrigation
- Rub the treated area until the appearance of a clean dermis or subcutaneous tissues with pinpoint bleeding
- To remove remnants of dissolved eschar, apply a dressing soaked with an antibacterial solution for at least 2 hours
Second Application of NexoBrid1
- A second application of NexoBrid may be applied 24 hours following the first application to either the same area previously treated with NexoBrid, or to a new area. A second application may be considered if:
- The wound area is more than 15% BSA, or
- Multiple wound areas on different body surfaces require two treatments for logistical reasons such as body position, or
- The first application’s eschar removal was not complete
- The total treated area must not exceed 20% BSA, inclusive of both applications
NexoBrid may lead to more precise wound depth determination.3,7
The post-NexoBrid wound bed may reveal a shiny, healthy white dermis with pinpoint bleeding, similar to the appearance of a freshly harvested donor site.8
- Burns originally deemed as “mixed” or “deep” may be reassessed as only superficial or partial thickness with viable dermal layers capable of re-epithelialization9
- The distribution of any full thickness defects within the burn may be clearly diagnosed, as well as the other levels of injury with the exposure of underlying structures7,10
- Selective eschar removal with NexoBrid may reveal a clear view of the extent of the original injury7,10
- Optimal wound management begins with accurate determination of wound depth111,12
- After NexoBrid, these assessments can be made according to the vascular patterns and colors which may coincide with relevant structures of the dermis and subcutaneous layer7,10
Before NexoBrid
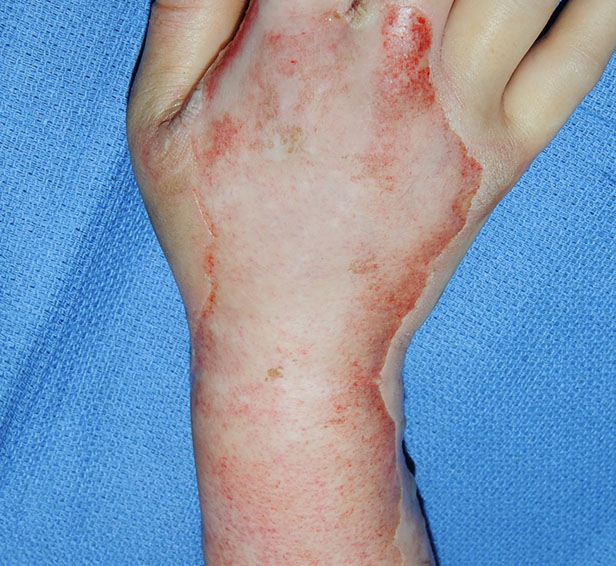
Post Burn Day 2: Wound appearance evaluated as containing a full thickness component by treating surgeon.
After NexoBrid
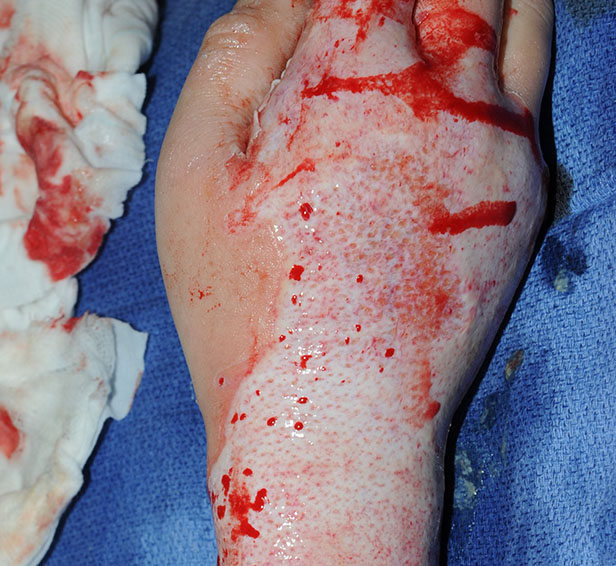
Post Burn Day 3: After eschar removal with NexoBrid, a shiny, white dermis was revealed with superficial, deep dermal and full thickness components.
Images are from a real NexoBrid patient
The Visual Diagnosis Scale7,12–14
After NexoBrid, wound depth may be determined according to vascular patterns and colors. The vascular patterns and colors coincide with relevant structures of the dermis and subcutaneous layers, including the blood vessels and hair follicles throughout various dermis depths.7,10,15
To improve depth diagnosis, a specific visual scale was developed by a working group from the Burn Unit in Ghent, Belgium. An additional illustration of a skin representation is show to support the scale.7,12–14
- The scale was developed by studying and comparing pre-NexoBrid photos, pre-NexoBrid LDI scans, post-NexoBrid photos, post-soaking photos, treatment, follow-up photos, and time to wound closure7,12–14
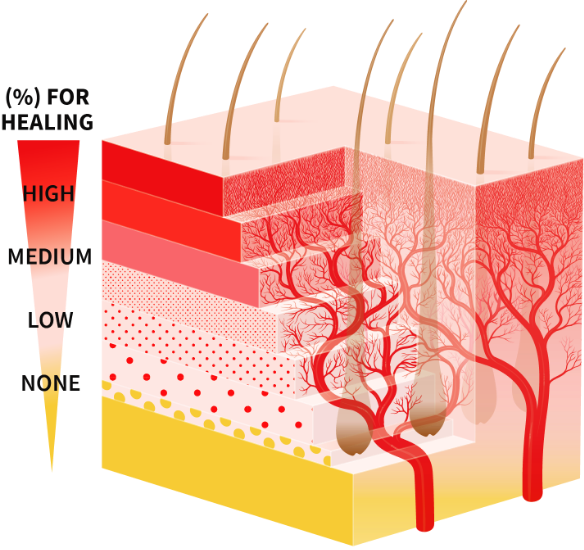
This Visual Diagnosis Scale is being provided for information purposes only. It is not used as part of the standard of care or as a validated scale. It was used to initiate a burn center into the DETECT and NEXT Clinical Trials as well as for education during wound bed diagnosis after treatment with NexoBrid.7,12
Burn Depth Diagnosis7,12
The post-NexoBrid wound bed is different in appearance from wounds that have been surgically excised. The following clinical examples detail what has been seen after eschar removal with NexoBrid.7,12
Papillary Dermis7,12
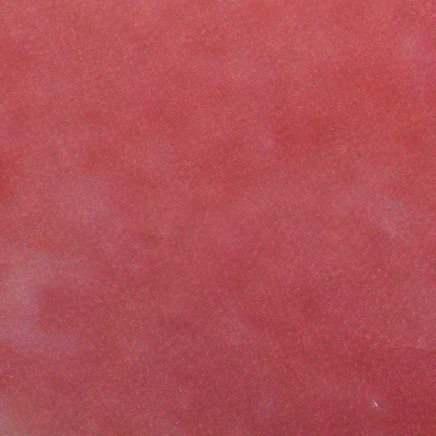


Papillary Dermis7,12
A uniform red color (with no visible circles) remains as a result of an abundance of capillaries.
High chance for spontaneous re-epithelialization
Images are from real NexoBrid patients treated outside of the U.S. following standard application protocol. Individual results may vary.
Reticular dermis7,12
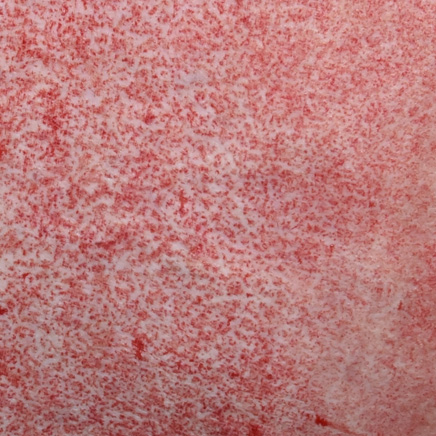

Reticular dermis7,12
A white color remains due to an abundance of collagen with small-to-medium pinpoint bleeding circles and some potential for translucent and visible fat.
Medium-to-low chance for spontaneous re-epithelialization
Images are from real NexoBrid patients treated outside of the U.S. following standard application protocol. Individual results may vary.
Subcutaneous Fat7,12
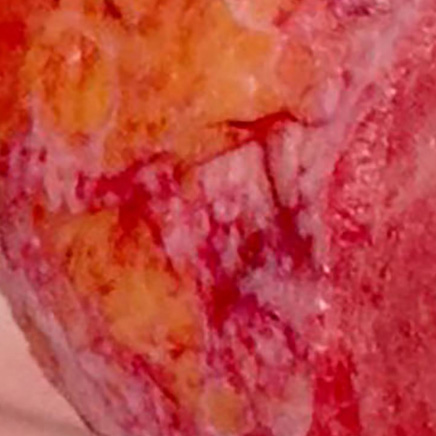

Subcutaneous Fat7,12
Large pinpoint bleeding circles, visible fat, and blood vessels remain.
No chance for spontaneous re-epithelialization
Images are from real NexoBrid patients treated outside of the U.S. following standard application protocol. Individual results may vary.
- Soak the wound to remove all remains of NexoBrid and dissolved eschar16
- After soaking, immediately cover the wound with moist dressings to prevent desiccation16
- Dress wound(s) sterilely according to burn center protocols
Wound care considerations

Deep partial thickness wound

Mixed depth wound
(spontaneous healing)

Mixed depth wound (autograft)

Full thickness wound

